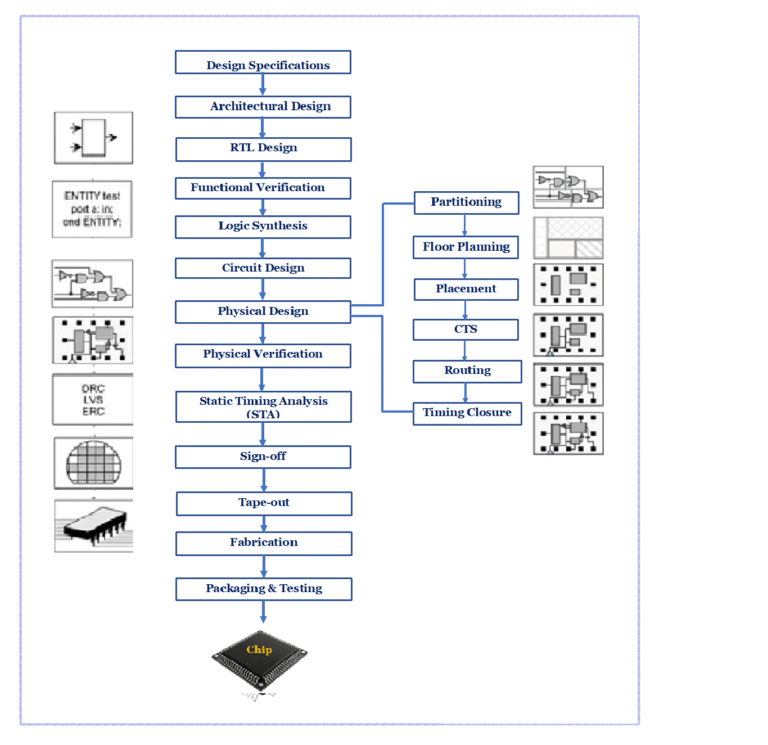
Introduction to IC technology
Integrated Circuit (IC) technology refers to the process of fabricating millions (or even billions) of components—such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors on a single chip of silicon. ICs revolutionized electronics by enabling miniaturization, high speed, low power consumption, high reliability, and low cost per function.
IC technology forms the foundation of all modern electronic systems including processors, memory devices, sensors, embedded systems, and VLSI chips.
Why IC Technology is Important?
IC technology enables:
- High-performance computing
- Low-power portable systems
- High-density memory and storage
- Artificial Intelligence and IoT advancements
- Reliable semiconductor manufacturing
- Less time-to-market
- Low cost
IC technology advances consumer electronics, automotive systems, medical devices, communication equipment, aerospace, and defense applications forward through constant scaling and innovation.
Evolution from discrete components to ICs
| Stage | Technology | Key Characteristics |
| 1 | Relays (1920s) | Large, slow, generated significant heat, consumed a lot of power |
| 2 | Vacuum Tubes (1940s–1950s) | Large, fragile, high power, low reliability |
| 3 | Invention of transistor (1947) | smaller, more reliable, and required less power |
| 4 | Discrete Transistors (1950s–1960s) | Smaller and faster, but manual wiring required |
| 5 | invention of the integrated circuit by Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments and Robert Noyce at Fairchild Semiconductor | First prototype IC |
| 6 | Small-Scale Integration — SSI (1960s) | Tens of transistors per chip |
| 7 | Medium-Scale Integration — MSI (1970s) | Hundreds of transistors per chip |
| 8 | Large-Scale Integration — LSI (1980s) | Thousands of transistors per chip |
| 9 | Very Large-Scale Integration — VLSI (1990s–2000s) | Millions of transistors per chip |
| 10 | ULSI & Beyond — System-on-Chip (SoC) (2000s–Present) | Billions of transistors integrated on a single chip |
IC Integration Levels
| Generation | Full form | Approx. Transistor count |
| SSI | Small Scale Integration | 1 – 10 |
| MSI | Medium Scale Integration | 10 – 100 |
| LSI | Large Scale Integration | 100 – 10000 |
| VLSI | Very Large Scale Integration | 10,000 – 1 million |
| ULSI | Ultra Large Scale Integration | 1 million – 100 million |
| GSI | Giga Scale Integration | Billions (10⁹+) |
| WS/WSI | Wafer Scale Integration | Entire wafer as one IC |